Head Injury Pictures
Head injury is also known as traumatic brain injury and craniocerebral trauma. Brain injury occurs due to outside force. A common incidence of head injury is a motor vehicle accident. Head injury is a special issue in developing countries and causes mortality and morbidity. In this artical fully explane with Head Injury Pictures and Head Injury Digrams.
head injury pictures explication
Head injury is defined as the injuries to the head due to trauma to the scalp, skull and brain. Head injury caused acute, chronic, and life-threatening neurological issues. in this artical Head Injury Pictures are brodely explanne with Head Injury Pictures and every student easly lern about Head Injury Pictures Concussion this artical are nursing Students.
Types of head injury
- Open head injury Pictures
- Closed head injury Pictures

Open head injury
- Open head injury breaks the scalp and skull and is observed by nude eyes.
- Open head injuries are – scalp injury
- Skull bone injury
- Injury in meningitis as layers.
Closed head injury
- Closed head injury does not break the skull and cannot be seen with the naked eyes.
- Closed the head injury – concussion
- Cerebral contusion
- Epidural hematoma
- Subdural hematoma
- Intracerebral hamartoma.
-
Concussion –

the vibration of brain and cranial cavity. Direct below to the head and violent shaking of the head. Transient interruption in brain activity and no structural injury.
- Cerebral contusion – Brushing and laceration of the brain tissue within cranial cavity associated with swelling.
-
Epidural hematoma –
a collection of blood between the dura mater and skull bone due to injury. Collection blood due to meningeal artery trauma. It is a most common type of intracranial hemorrhage. It is a surgical and neurological emergency.
-
Subdural hematoma –
a collection of blood between the dura mater and arachnoid space. Venous blood accumulated due to injury. Hematoma may be slower to develop. Subdural hematoma related to acceleration deceleration injury.
- Intracerebral hematoma – Bleeding into the brain tissue commonly associated with edema.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage – Collection of blood between arachnoid space and pia mater due to injury.
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage associated with CSF accumulation.

Head Injury Causes
- Accident (motor vehicle accidents)
- Falls and assault
- Domestic and industrial hazards
- Sports accidents
- Occupational accidents
- Gunshot.
Clinical Manifestation
- Altered LOC (level of consciousness)
- Dilated pupils
- Loss of normal eye movement
- Increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
- Headache, vertigo
- Nausea and vomiting
- Airway affect
- Dizziness, weakness and restlessness
- Change in the body temperature
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Comma and seizures
- Trouble walking and speaking
- Scalp injury and breathing
- Sensory and motor function loss.
- Ear, nose and mouth secretion
- Swelling and bruising of the brain.
Diagnosis of Head Injury
- History collection and physical examination.
- CT scan and MRI.
- X-ray ( radiography)
- Glasgow Coma scale (GCS) – assess level of consciousness.
- Neurological assessment.
- EEG and brain scan.
- Ultrasonography imaging.
Head Injury Treatment
- Maintain patient ABC (Airway, breathing, circulation)
- TT injection
- Pharmacological management –
- Osmotic diuretics – mannitol to reduce increased ICP.
- Steroids – for inflammation and decrease edema.
- Antihypertensive – for decrease BP.
- Anti-seizure medication.
- Mild analgesics
- Antibiotic therapy for infection.
- Antipyretics drugs.
- Morphine sulphate.
- Patient on NPO.
- Administer IV line.
- Nasogastric tube administer.
- Catheterization method.
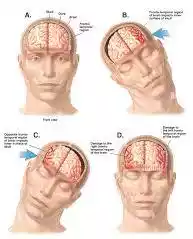
Surgery of Head Injury
Craniotomy – removal of hematoma by incision into the cranium.
Complication Head Injury
- Increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
- Coma and Seizures
- Hydrocephalus and brain herniation
- Permanent neurological deficits
- Paralysis and chronic headache
- Altered neurological behavior
- Death.
Nursing Management Head Injury
- Nurses monitor patient head injury type and control haemorrhage by cover and applied pressure dressing.
- To clean wounds by an antiseptic solution.
- Check the patient Airway, breathing, circulation (ABC) and vital signs.
- Provide a comfortable position (head elevated 30° angle and maintain neutral neck).
- Airway clearance by removing secretions.
- Maintain patient NPO and provide fluid by IV line or food provided by NG tube.
- Nurse monitor increased ICP and cerebral edema.
- After head injury, the nurse will monitor glucose tests from body secretion to identify CSF leakage.
- Nurses maintain the Seizures precautions.
- The nurse will prepare the patient for surgery.
- The nurse will check the level of consciousness of the patient with the help of Glasgow Coma scale.
- Nurses monitor the neurological status of patients.
- Provide health education.

Key Points head injury pictures
- What is another name for head injury – Craniocerebral trauma?
- The most common reason for head injury – Motor vehicle accidents.
- What is the head injury that can be observed with naked eyes – Open head injury.
- A head injury consists of provision and laceration of the brain tissue – Cerebral contusion.
- Collection of blood between the skull bone and dura mater – Epidural hematoma.
- Collection of blood between dura mater and arachnoid space – Subdural hematoma.
- Collection of blood between space and pia mater – Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Common finding associated with head injury – Increased ICP.
- Common finding associated with increased ICP – Altered LOC.
- Level of consciousness assessed by – the Glasgow Coma scale.
- Most common surgery for head injury – Craniotomy.
- The common position provided when ICP is increased – Head and elevated 30° angle.
- If Glasgow Coma scale finding less than 7 – Severe head injury.
- Drug of choice for increased ICP – Mannitol.
- Epidural hematoma include the – Arterial blood.


















