What is Rheumatoid arthritis:-
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes symmetrical polyarthritis.
- Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints.
- Rheumatoid arthritis awareness day is celebrated on 2nd Feb.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a most common systemic inflammatory disease characterized by symmetrical joint involvement.
Rheumatoid arthritis Definition
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that include inflammation in the membrane lining of the joint and produce an inflammatory synovitis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis generally involves small, peripheral and systemic or non-weight wear joints.
- Commonly prevalence between the age of 30 – 50 years.
Cause of Rheumatoid arthritis
- Idiopathic
- Genetic factors
- Environmental exposure
- Immunological factor
- Autoimmune disorder
- Endocrine imbalance
- Inflamed synovium
- Tumour necrosis factor
- DM, obesity
- Lack of exercise
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Smoking
- Bacterial and fungal infection
- Antigen dependent activation of T- lymphocytes.
- Metabolic imbalance.
Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid arthritis
Cause / immunological / autoimmune
↓
Inflammation of synovial membrane of joint
↓
Antigen and antibody reaction
↓
Damage the articular cartilage
↓
More production of granular tissue and edema
↓
Decrease joint mobility
↓
Deformity.
Stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Stage – I
– Preclinical stage
– Non sign symptoms
– Increased ESR, C – reactive protein.
Stage II
- Synovitis stage involves inflammation in the synovial membrane.
- Show sign symptoms.
- ADL affects.
Stage III
- Destruction stage
- Daily living activity affect
- Both bones rub together and cause pain and swelling.
Stage IV
- Deformity stage
- End stage of rheumatoid arthritis
- Loss of joint functions.
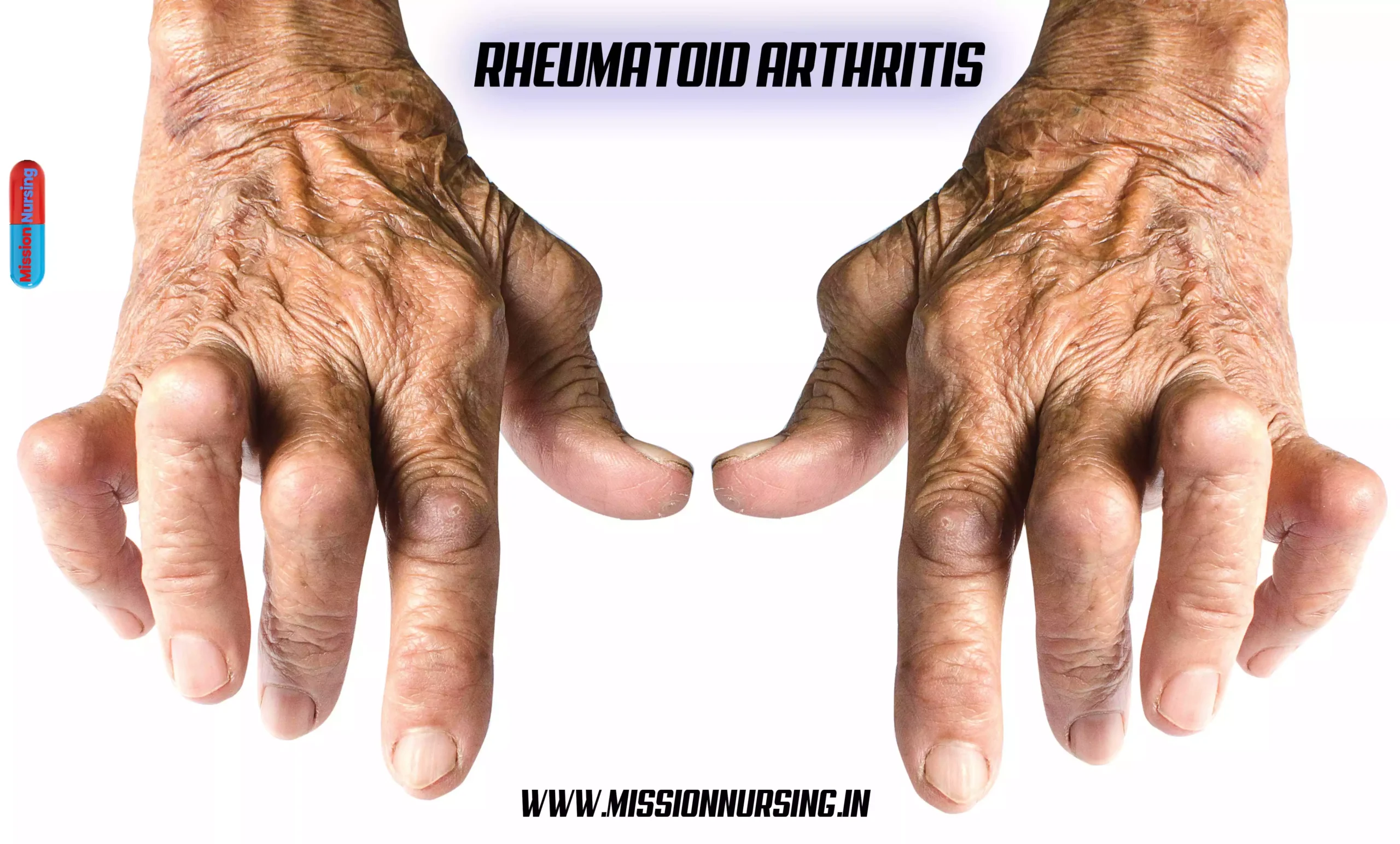
Sign and Symptoms of Rheumatoid arthritis
- Swelling and edema in the joints.
- Morning joint stiffness.
- Sever pain
- Tenderness or redness
- Deformity of joints ( loss of anatomy )
- Reduce range of motion
- Muscles pain
- Rheumatoid nodules
- Low grade fever
- Fatigue and weight loss
- Swan neck deformity
- Polyarthritis and joint warmth.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid arthritis
- History collection and physical examination.
- Joint x-ray ( show deformities )
- Blood test – increase ESR, increased C reactive protein.
- CT scan and MRI.
- Anti citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs).
- History of infection.
Treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis
- NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and Aspirin used for pain.
- Corticosteroids drugs – prednisolone (anti-inflammatory)
- Topical analgesics (zostrix)
- Immunosuppressive agents – methotrexate
- Antirheumatic drugs – D. Penicillin
- Chloroquine.
- Disease-modifying ant rheumatic drugs (DMARD).
Surgical Management
- Arthroplasty – joint replacement surgery.
- Arthroscopy – is a surgical procedure on a joint to examine and treatment of damaged tissue by using arthro.
- Synovectomy – remove inflamed joints tissues.
Nursing Management
- Nurses monitor vital signs and joint immobility.
- Assess small and peripheral joints are affected.
- Assess patient range of motion.
- Help to reduce morning joint stiffness, provide hot tea and hot bath.
- Nurses provide a variety of comfort levels.
- Provide rest, heat and cold application of message to reduce pain.
- The Administrator prescribed medication.
- Nurses encourage patients to verbalize feelings about pain and stiffness.
- Identify causing emotional and physical factors that cause fatigue.
- Nurses encourage independence in mobility or activity and assist them.
- Nurse conduct counselling for self-care activity.
- Provide physiological and emotional support.
- Nurses provide health education.
Key Points
- Inflammation in the joints – Arthritis.
- Autoimmune joint disorder involves synovitis – Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is more severe in – Women.
- Which type of joints are involved in rheumatic arthritis – Non weight wear joints.
- Which stage of rheumatoid arthritis involves the deformity – Stage IV.
- In which disorder is the swan neck deformity seen – Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Surgical joint replacement – Arthroplasty.
- Morning joint stiffness reduced by – Hot tea and hot bath.
- Surgical removal of infected joint tissue – Synovectomy.
- Rheumatoid arthritis deformity assessed by – Radiological examination (x-ray).