female external genitalia organ
The human organ system is made up of several organs which is necessary for the proves of reproduction.
- Female Reproductive system Divided into: –
- External Genitalia
- Internal Genitalia
- Accessory reproductive organ.
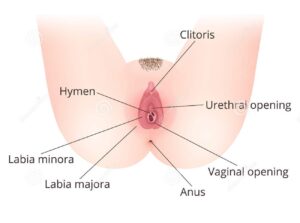
-
External Genitalia organ lists
- External Genitalia is also known as the “Vulva” and pudendum.
- External Genitalia consists of the all Externally visible genitalia organs in the perineum.
- External Genitalia Consists of the following: –
- Mons Pubis
- Labia majora
- Labia Minora
- Hymen
- Clitoris
- Vestibule
- Urethra
- Skin’s gland
- Bartholin’s gland
- Vestibular bulbs
-
Mons Pubis
Mons pubis is the pad of subcutaneous adipose connective tissue and covered by hair.
- Mons pubis hair pattern is triangular
-
Labia majora
- Labia majora Enclose and protect the External genital organ.
- Vulva consist the elevation of skin and subcutaneous tissue, which is from the labia majora.
- Labia majora same like as “Large lips”.
- Labia majora contains – sweat gland & sebaceous glands.
- Labia majora Homologous to sacrotum in the male.
-
Labia minora
- Labia minora is small fold of skin and cover by labia majora.
- Labia minora join superiorly by frenulum and prepuce and Inferiorly join with fold of fourchette.
- Labia minora have no contains of hair follicle or sweat glands, only include sebaceous gland.
- Labia minora Homologues to the penile urethra of male.
Clitoris
- Clitoris is the small cylindrical erectile body about 1.5-2cm.
- Clitoris situated in the most anterior part of vulva.
- Clitoris consist a gland, a body, and two crura.
- Clitoris more sensitive part in the vulva to stimulation and can become erect During excitement.
- Clitoris homologous to the penis in the male
-
Vestibule
- The vestibule is the triangular space bounded with
Anteriorly – by clitoris
Posteriorly – by fourchette
Laterally – by labia minora
- Vestibule include the – urethral opening
- Vaginal orifice and hymen
- Ducts from the greater vestibule
- Skene’s gland
- Urethral opening – situated in midline Infront of the vaginal orifice.
- Urethral opening 1-1.5cm below the public arch.
Vaginal orifice and Hymen
- Vaginal orifice and hymen situated in the posterior end of the vestibule.
- Hymen is a thin fold of vascularized mucous membrane.
- Hymen located just inside the vaginal opening.
- Hymen rupture usually following the first sexual intercourse.
- Bartholin’s gland
- Bartholin’s gland also knows as greater vestibular gland
- There are 2 Bartholin glands, situated one on each side.
- Bartholin gland pea sized and yellowish-white color.
- During sexual Excitement occur in Bartholin gland.
- Bartholin gland homologous to the bulb of penis in the male.
- Bartholin Duetà Bartholin Duet is 2cm long and open into the vestibule.
- Skene’s gland–
- Skene’s glands are the largest paraurethral gland.
- Skene’s glands are homologues to the prostate in the male.
Blood supply of External genitalia
- Artery – Branch of the internal pudendal artery
- Veins – Internal pudendal vein
– long saphenous vein
– Vaginal venous plexus
- Nerve supply – Pudendal nerve
The function of the External genital organ of female
- Protect the internal genital organ
- Prevent the infection
- Enable the sperm to enter the body.
External genital organ assesses by USG in fetal age, at the – 12week of gestational
Internal gonad assessments by USG at the – 8week of gestational
QnA:-
- Female labia majora homologues to – Sacrotum in male.
- Labia minora consists only – The sebaceous gland.
- Most sensitive part in vulva During the sexual Excitement is – Clitoris.
- Clitoris is homologue to the – Pelvis In the male.
- A most common cause of hydrocephalous – Imperforate hymen.
- The Bartholin gland is also known as the – Greater vestibular gland.
- Which epithelium occurs in the Bartholin gland – Cuboidal epithelium.
- External genital organ assessed by USG in fetal age at the – 12 week of gestational.
Also Read. Female Internal Genital Organ


















1 thought on “female external genitalia”